SSO Using SAML 2.0 - Comprehensive Guide
TL;DR
- This article covers everything you need to know about implementing single sign-on (SSO) using SAML 2.0. Included is an explanation of SAML's core concepts, how it works, and how it compares to other SSO protocols like OAuth and OpenID Connect. It also provides practical guidance on configuration, security best practices, and troubleshooting common issues, useful for IT professionals looking to enhance their organization's authentication infrastructure.
Understanding SSO and SAML 2.0: The Basics
Alright, so you're juggling multiple apps and passwords, huh? It's a pain, I get it. That's where single sign-on (sso) comes in. Think of it as one key to unlock all your digital doors.
- Definition: Sso lets you access multiple applications with just one set of credentials. No more password chaos!
- User Experience: It seriously cuts down on password fatigue. I mean, who enjoys resetting passwords every other day?
- Enhanced Security: Centralized authentication means fewer entry points for bad actors. It's like fortifying the main gate instead of every window.
Okay, so how does it all work? That's where SAML 2.0 jumps in. It's the protocol that makes sso tick.
- Definition: Saml 2.0 facilitates secure authentication and authorization. Basically, it's how your identity gets verified across different services.
- Key Players: Think of an Identity Provider (idp) – that's who confirms you are who you say you are – and a Service Provider (sp) – that's the app you're trying to use.
Now, what about other protocols like OAuth and OpenID Connect? Those are for different use cases, but they also help with authentication and authorization. We'll stick to SAML for now.
How SAML 2.0 Works: A Step-by-Step Walkthrough
Ever wonder how you seamlessly jump between apps at work? Well, SAML 2.0 is often the unsung hero making that magic happen! It might sound complex, but let's break down how it actually works, step by step.
Here's the basic dance:
- First, a user tries to access an app (the service provider, or sp). Think, say, accessing your salesforce account.
- The sp then asks the identity provider (idp) to authenticate the user. It's like showing your id at the door.
- The user authenticates with the idp. This is where you might enter your username and password, or use multi-factor authentication.
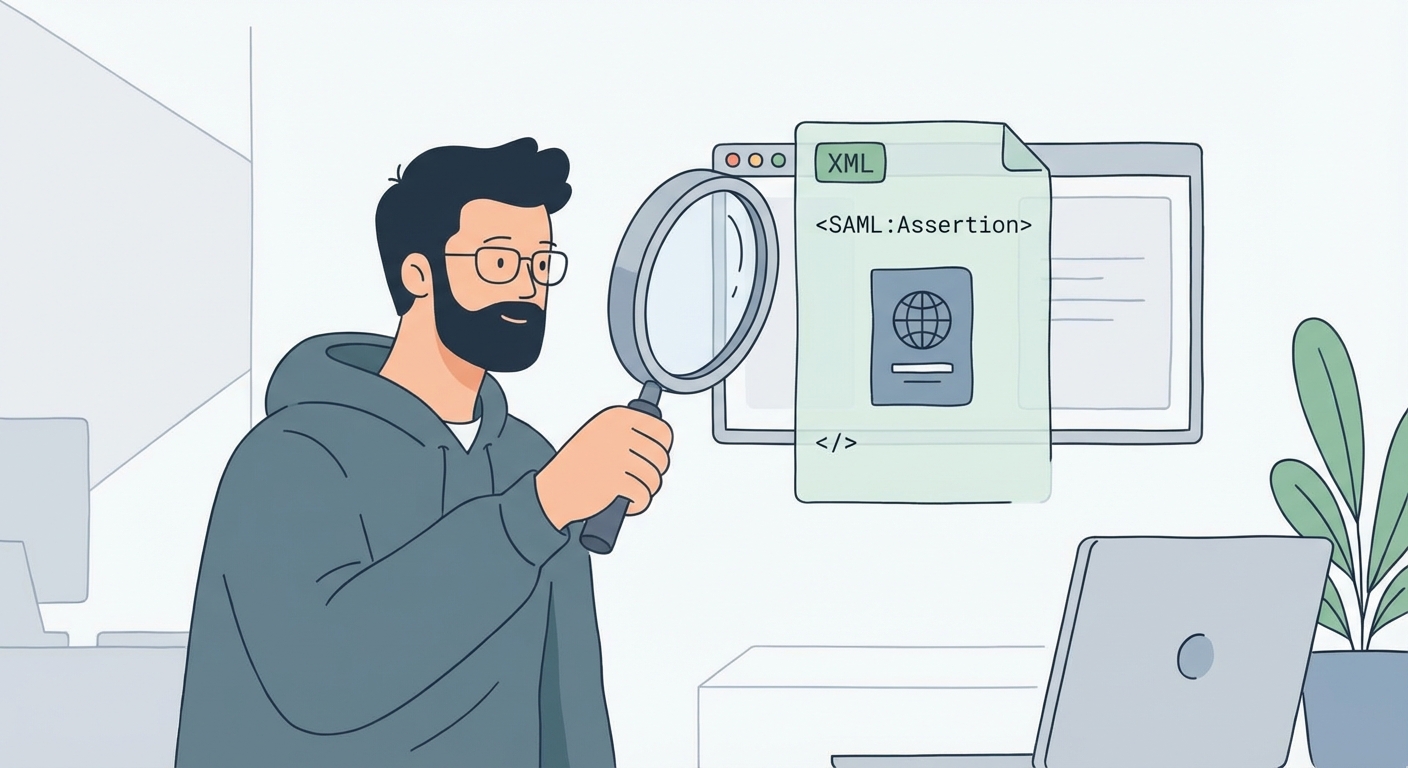
- The idp sends a SAML assertion back to the sp. It's a signed statement saying, "yep, this user is who they say they are".
- This assertion is like a digital passport. It contains crucial information:
- Issuer: Who's vouching for you (the idp).
- Subject: Who is the user being identified.
- Conditions: Rules for when the assertion is valid, like time limits.
- Attributes: Extra info, like roles or permissions.
- This assertion is like a digital passport. It contains crucial information:
- Finally, the sp validates the assertion and grants access. Voila! You're in.
SAML 2.0 uses different "bindings" for sending messages. Two common ones are HTTP Redirect and HTTP POST.
- HTTP Redirect Binding: This is generally used for sending SAML requests. The request is encoded and appended to a URL, which the browser then follows. It's good for shorter messages.
- HTTP POST Binding: This is typically used for sending SAML responses. The assertion is embedded in an HTML form that's automatically submitted by the browser. It's better for larger amounts of data. Choosing the right one is key for compatibility and security.
So, what's next? Let's dive into getting this all set up.
Configuring SAML 2.0: A Practical Guide
Ever tried setting up sso and felt like you're wrestling an octopus? Yeah, it can be a mess, but getting SAML 2.0 configured right is worth the effort. Think of it as building a secure bridge between your apps and your users.
First, you gotta choose an identity provider (idp), like Azure ad or Okta. Then, you'll need to configure it with your service provider (sp) metadata – that's the entity id and acs url. Don't forget to setup your user accounts and groups in the idp, otherwise no one's getting in!
Next, on the sp side, you'll want a saml library or toolkit. Python-saml is pretty useful, and OpenSaml is another solid choice. Configure the sp with the idp's metadata – entity id, sso url, the whole shebang.
Attribute mapping and session management is key, too. This means you need to tell the sp what user attributes (like name, email, or role) it should expect from the idp and how to use them to create a user session. It's how the sp knows who you are after the idp says you're good.
Generating sp metadata and feeding it to the idp is crucial. Then, grab the idp metadata and plug it into your sp. Make sure everything matches up; consistency is key to avoid headaches. According to Microsoft's identity platform documentation, the issuer element in an authnrequest must exactly match one of the serviceprincipalnames in the cloud service in microsoft entra id.
Next up, we'll tackle troubleshooting common saml issues, so you're not left scratching your head.
Security Best Practices for SAML 2.0
Alright, so you're all in on SAML 2.0, that's great. But, are you really doing it right? Securing your setup isn't just a checkbox, it's gotta be a mindset.
- Certificates are Key: These are used to digitally sign SAML assertions and messages, proving their authenticity.
- How to manage: You'll typically generate a public/private key pair for your idp and sp. The public key is shared, while the private key is kept secret. Regularly rotate these certificates to limit the impact of a compromised key. Think of it as the foundation of trust.
- Prevent Replay Attacks: This is when an attacker intercepts a valid SAML assertion and tries to reuse it.
- How to prevent: Time-limited tokens and invalidating them after use is a must. Assertions should have a short validity period (e.g., a few minutes), and the sp should keep track of used assertion IDs to prevent reuse. Otherwise, it's like leaving the door unlocked after you've left.
- MFA is Your Friend: Hooking up multi-factor authentication? Adds a crucial layer; it's like having a guard dog and an alarm system.
Next up? Tackling common SAML issues.
Troubleshooting Common SAML 2.0 Issues
Okay, so you've navigated the saml maze, huh? Bet you're itching to wrap this up and put it all into action. Let's make sure it all comes together smoothly.
- Double-check configs: Mismatched urls or entity ids? A classic gotcha. As noted in the configuration section, Microsoft's documentation highlights the importance of issuer matching.
- Certificates are your friend: Expired certs are a major headache. Make sure your idp and sp certificates are valid and correctly configured on both sides.
- Test, test, test: Don't skip testing various scenarios; different user roles, error handling. Use browser developer tools to inspect SAML requests and responses if you're stuck.
Honestly? Getting saml right feels good. Onwards and upwards!